What is the Difference Between Coal Peas and Coal Small Nuts
- National Coal Suppliers

- Jul 23, 2025
- 9 min read
Updated: Aug 30, 2025
Explore coal peas and small nuts differences, industrial applications, combustion efficiency, and best practices to optimize boiler performance and reduce operational costs.
About the Author: National Coal Suppliers is a trusted source for 10,000+ monthly readers seeking industry insights on coal mining, gold, and chrome. Backed by industry analysts and technical writers, we provide accurate data on grades, specs, and sourcing of coal types, including peas, small nuts, and duff, serving buyers, exporters, and energy firms.

Key Takeaways:
Coal peas (6–25 mm) and small nuts (25–50 mm) differ in size, affecting boiler compatibility and combustion performance.
Coal peas ignite faster and burn more efficiently, making them ideal for pulverized and fluidized bed boilers.
Small nuts suit grate and stoker boilers, offering longer burn times but producing more ash and clinker.
Proper storage and moisture control are essential to maintain coal quality and optimize combustion.
Choosing the right coal size improves fuel efficiency, reduces emissions, and minimizes maintenance costs.
STRUGGLING TO OPTIMIZE YOUR COAL SUPPLY? We help industrial operations source the right coal size for peak boiler performance and lower costs. Our expert guidance simplifies fuel decisions. Contact us to get started today.
Selecting the right coal size is crucial for industrial boilers and processes. Coal peas and coal small nuts are two commonly used coal grades with distinct characteristics that affect combustion efficiency, boiler performance, and operational costs.
Understanding the differences between coal peas and coal small nuts helps industries optimize fuel consumption, reduce maintenance issues, and comply with environmental regulations. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, selecting the appropriate coal size is critical to optimizing boiler efficiency and reducing emissions in industrial applications (EIA, 2023).
This article explores their physical properties, industrial applications, combustion efficiency, and practical handling tips to guide buyers and plant operators in making informed decisions.
What Are Coal Peas and Coal Small Nuts?
Choosing the right coal size is key for efficient industrial combustion. Two common grades are coal peas and coal small nuts, each with distinct size ranges and uses. Understanding their basic definitions helps clarify why different boilers and processes prefer one over the other.
Here’s a quick breakdown of these coal types:
Coal Peas: Coal particles sized between 6 mm and 25 mm. They are small and fairly uniform, making them ideal for combustion systems that require finer fuel for better burn control.
Coal Small Nuts: Larger coal pieces ranging from 25 mm to 50 mm. These coarser chunks suit boilers built to handle bigger fuel sizes and slower combustion rates.
Property | Coal Peas | Coal Small Nuts |
Size Range (mm) | 6 - 25mm | 25 - 50mm |
Typical Uses | Pulverized boilers, fluidized beds | Grate and stoker boilers |
Combustion Rate | Faster | Slower |
Ash Content (avg.) | 5–12% | 6–14% |
Moisture Content (avg.) | 8–12% | 8–15% |
Coal grading standards from ASTM D388 and ISO 11760 classify coal sizes consistently. Coal suppliers often provide technical datasheets specifying these ranges to match customer needs precisely. Learn more about all the industries that use small nuts for steam boilers?
Why Coal Size Matters: Impact on Industrial Boilers
Boiler systems depend heavily on coal size for:
Fuel feed mechanism compatibility: Small coal (peas) flows smoothly in pulverized systems; larger chunks (small nuts) are better for grate stokers.
Combustion efficiency: Smaller sizes ignite faster and burn more completely, improving heat output.
Emission control: Finer coal sizes reduce unburnt carbon emissions but may increase dust.
Maintenance and ash management: Larger coal often produces coarser ash, increasing clinker risk but easier to manage in some settings.
For example, a power plant using a pulverized coal boiler requires consistent coal peas for steady pulverization and combustion. Meanwhile, a cement kiln using a stoker grate may prefer small nuts for longer combustion times and easier fuel handling. Learn more about the diffirence off RB1, RB2 and RB3 coal.
Detailed Comparison of Coal Peas vs Coal Small Nuts Characteristics
Choosing the right coal size is critical for industrial operations that rely on efficient and reliable fuel sources. Coal peas and coal small nuts are two common grades, each with distinct physical and chemical properties that influence combustion performance, boiler compatibility, and overall operational costs.
Understanding these differences helps plant operators optimize fuel use and minimize maintenance issues. In the following section, we provide a detailed comparison of coal peas vs coal small nuts characteristics, focusing on size, combustion behavior, and quality metrics essential for industrial applications. Learn more on how to improve boiler efficiency.
Physical and Chemical Differences
Calorific Value: Both types generally have similar energy content, but moisture and ash content variations affect net heat output. Coal peas often have slightly lower moisture, resulting in better thermal efficiency.
Moisture Content: Small nuts tend to retain more moisture due to larger surface areas and stacking methods. Moisture over 12% reduces combustion efficiency significantly.
Ash Content: Small nuts typically generate more ash and clinker, requiring more frequent cleaning and monitoring.
Sulfur Content: Varies by coal source rather than size but is crucial for emission compliance.
Performance Table Summary
Feature | Coal Peas | Coal Small Nuts | Impact on Boiler |
Size uniformity | High | Moderate | Better combustion control with peas |
Ignition speed | Fast | Moderate | Faster steam generation with peas |
Ash and clinker | Lower ash, less clinker | Higher ash, more clinker risk | Increased maintenance with small nuts |
Handling ease | Smooth feed, less blockages | Potential feed blockages | Risk of downtime if poorly handled |
Best Coal Size for Industrial Boilers
Choosing the right coal size is essential for maximizing industrial boiler efficiency and reducing operational issues. Coal peas and coal small nuts are two common grades that differ in size, combustion behavior, and suitability for various boiler types.
Understanding which coal size aligns with your boiler’s design and your industry’s needs can significantly impact fuel consumption, emissions, and maintenance costs. Below, we explore how to match coal size to boiler type for optimal performance.
1) Pulverized Coal Boilers
Require coal peas for efficient pulverization. These boilers burn finely ground coal and need uniform, small sizes to maintain steady combustion and reduce emissions.
2) Grate and Stoker Boilers
Designed for coal small nuts or larger sizes. These boilers handle coarser fuel with longer burn times. Coal small nuts reduce feed rate fluctuations and manage clinker formation better with proper ash removal systems.
3) Fluidized Bed Boilers
Prefer coal peas for uniform fluidization and heat transfer. Larger particles disrupt bed stability and reduce combustion efficiency.
Advantages of Coal Peas in Power Plants
Coal peas offer several distinct benefits that make them a preferred fuel choice for many power plants. Their size and physical properties contribute to more efficient combustion and smoother boiler operation. These advantages translate into cost savings, reduced emissions, and easier maintenance.
Key benefits of coal peas in power plants include:
Higher combustion efficiency due to faster ignition and burn rates.
Reduced unburnt carbon resulting in lower emissions and less waste.
Improved boiler responsiveness, allowing flexible load management.
Lower ash and clinker production reduce cleaning frequency and downtime.
Power plants prioritizing high efficiency and tight emission controls often specify coal peas to meet operational and regulatory demands. For example, a recent case study from a South African power plant showed a 5% fuel savings after switching to coal peas with better moisture control.

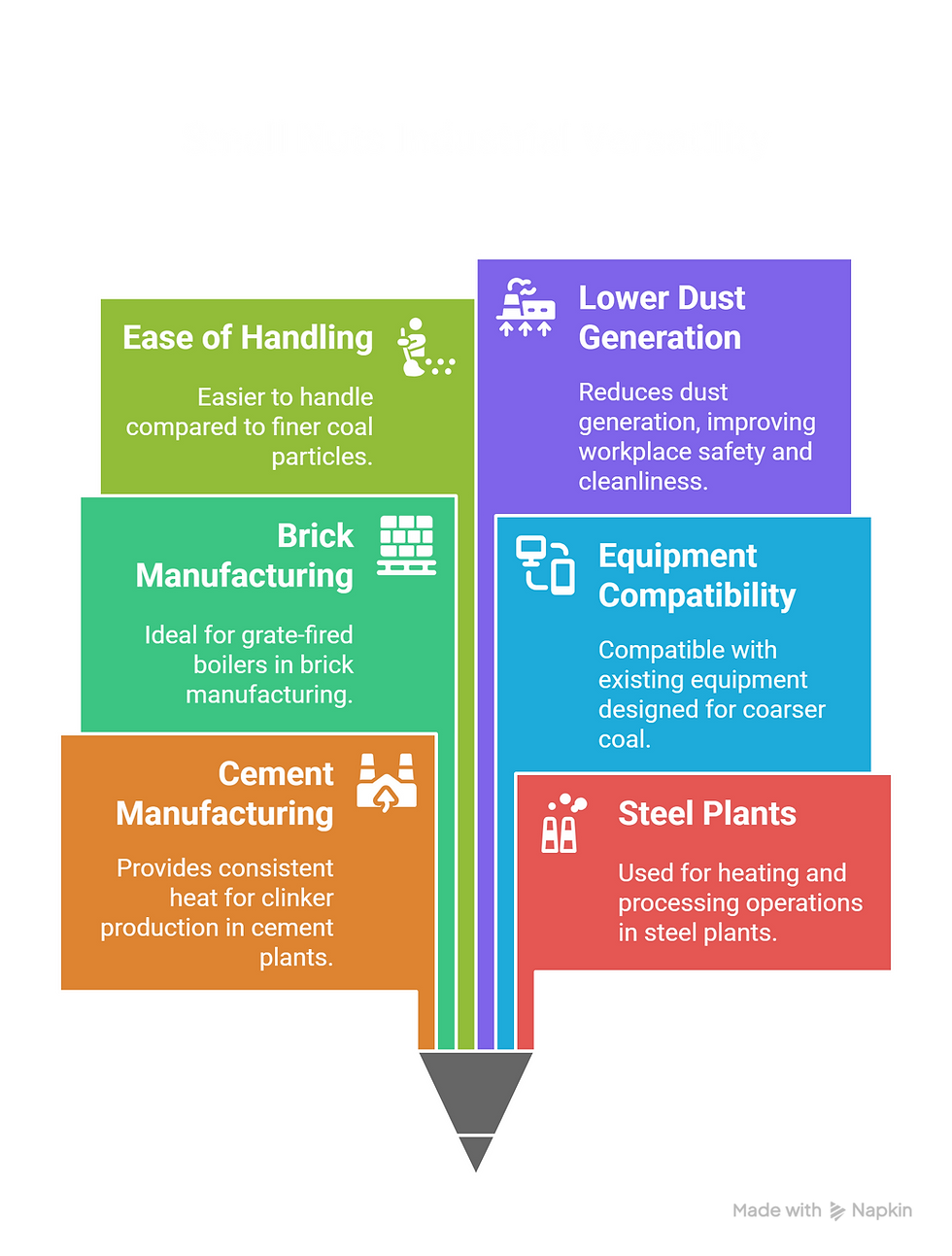
Industrial Uses of Coal Small Nuts
Coal small nuts play a vital role across several heavy industries due to their size and combustion properties. Their coarser particles provide steady, controlled heat release, making them ideal for processes that require slower, consistent burning. These qualities make coal small nuts a preferred fuel choice in specific manufacturing sectors where equipment compatibility and operational stability are priorities.
Key industrial applications include:
Widely used in cement manufacturing for consistent heat release during clinker production.
Common in steel plants for heating and processing operations requiring slower combustion.
Suited for brick manufacturing and other industries using grate-fired boilers.
Benefits include ease of handling, lower dust generation, and compatibility with existing equipment designed for coarser coal.
Coal Peas vs Small Nuts: Combustion Efficiency and Emissions
Coal peas generally achieve 90-95% combustion efficiency in pulverized boilers.
Small nuts range around 85-90% efficiency in grate stokers but may produce more particulate emissions if combustion is uneven.
Efficient air-fuel mixing is easier with coal peas due to size uniformity, reducing pollutants like CO and unburnt hydrocarbons.
Combustion Efficiency Chart (Hypothetical Data)
Coal Type | Combustion Efficiency (%) | CO Emissions (ppm) | Unburnt Carbon in Ash (%) |
Coal Peas | 93 | 120 | 3 |
Coal Small Nuts | 87 | 160 | 7 |
Operational Tips for Handling Coal Peas and Small Nuts
Proper handling of coal peas and small nuts is critical to maintain boiler efficiency and prevent downtime. Differences in size and physical properties mean each requires specific care in storage, feeding, combustion, and ash management. Following proven operational practices ensures consistent fuel quality, smoother combustion, and reduced maintenance.
Here are key tips to optimize handling of these coal sizes:
Storage: Keep coal dry under covered sheds to minimize moisture uptake. Coal small nuts require extra care due to larger surface areas prone to water absorption.
Feeding Systems: Regularly inspect conveyors and feeders for blockages, especially with small nuts that can jam more easily.
Combustion Control: Adjust air supply to match coal size for optimal burn. Use sensors to monitor flame stability and emissions.
Ash Management: Schedule ash removal to prevent clinker buildup; small nuts usually require more frequent cleaning.
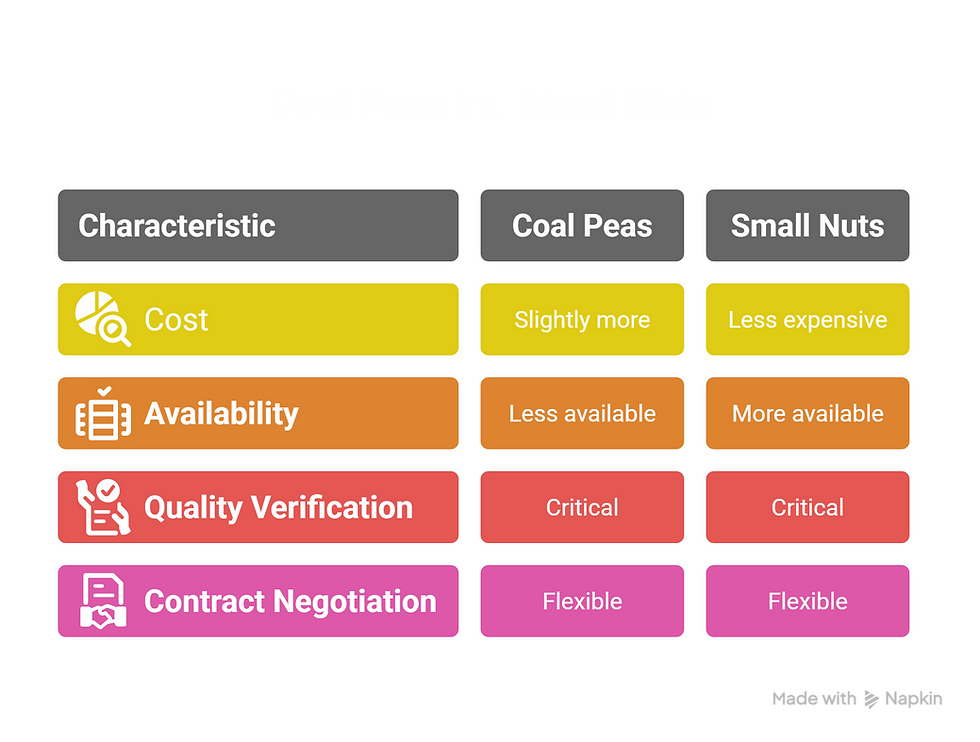
Cost and Supply Chain Insights
Understanding the cost and supply dynamics of coal peas and small nuts is vital for budgeting and ensuring a reliable fuel source. Prices can vary based on processing requirements, regional availability, and quality standards. Industrial buyers must also factor in the risks of low-quality coal impacting boiler efficiency.
Here are key considerations to help navigate the cost and supply chain effectively:
Coal peas often cost slightly more due to processing and size sorting.
Small nuts may be more readily available in certain mining regions.
Quality verification through third-party testing is critical to avoid low-grade coal that harms boiler performance.
Negotiate contracts with flexibility on quantity and delivery to adapt to seasonal supply changes.
Common Boiler Problems Linked to Coal Size and How to Fix Them
Clinker formation: Often caused by high ash content and large coal sizes. Reduce by blending coal or improving ash removal.
Inconsistent steam pressure: Linked to uneven combustion. Adjust coal feed and airflow to stabilize.
Excess ash accumulation: Use better coal sorting and frequent maintenance.
Feed blockages: Regularly clean feeders and conveyors; consider coal crushers if necessary.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Coal dust from peas requires dust suppression systems to protect worker health.
Both coal sizes produce CO2, SOx, and particulate emissions; combustion optimization reduces pollutants.
Comply with local environmental laws using scrubbers and filters.
Safe storage practices prevent spontaneous combustion risks, especially for small nuts due to moisture and heat accumulation.
Choosing Between Coal Peas and Small Nuts for Your Operation
Choosing the right coal size directly impacts boiler efficiency, maintenance, and emissions. Coal peas suit pulverized and fluidized bed boilers requiring fast, clean burns. Coal small nuts fit grate and stoker systems favoring slower combustion and easier handling. Evaluate your boiler type, fuel handling infrastructure, and operational goals carefully. For tailored advice and reliable coal sourcing, contact our experts today. Request samples or download our comprehensive guide to optimize your coal fuel strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ideal particle size range for coal peas and small nuts?
The ideal particle size range for coal peas is between 6 and 13 millimeters, while coal small nuts range from 13 to 25 millimeters. These sizes follow established industry standards to ensure compatibility with specific boiler types and fuel handling systems. Selecting the correct coal size improves combustion efficiency, reduces emissions, and minimizes equipment wear. Using the wrong size can cause blockages or incomplete burning, leading to operational inefficiencies and higher maintenance costs.
Can coal peas and small nuts be used interchangeably in boilers?
Coal peas and small nuts cannot be used interchangeably in most boiler systems because each size suits different combustion technologies. Coal peas are designed for pulverized and fluidized bed boilers, which require finer, more uniform fuel for efficient burning. Small nuts work best with grate and stoker boilers that handle coarser fuel and slower combustion rates. Using the incorrect size disrupts combustion stability, reduces boiler efficiency, and may cause mechanical issues or increased emissions.
How does moisture content affect coal small nuts combustion?
Moisture content in coal small nuts significantly affects combustion efficiency by reducing the net calorific value. Higher moisture requires additional energy to evaporate water before combustion, lowering heat output and increasing fuel consumption. Excess moisture also promotes incomplete burning, causing higher emissions of unburnt carbon and pollutants. Proper drying and storage techniques are necessary to keep moisture levels below 12%, ensuring optimal combustion, reduced emissions, and better boiler performance over time.
What safety precautions are necessary when handling coal peas and small nuts?
Handling coal peas and small nuts safely requires dust control measures, such as proper ventilation and personal protective equipment to prevent respiratory hazards. Storage areas must be monitored to prevent spontaneous combustion risks caused by heat buildup and moisture. Workers should follow established safety protocols, including safe coal transfer practices and emergency response plans. Regular inspections and training reduce workplace accidents and ensure compliance with health and safety regulations related to coal handling.
Are there environmental benefits to using coal peas over small nuts?
Using coal peas often results in environmental benefits compared to small nuts because peas burn more completely and efficiently, producing less unburnt carbon and particulate emissions. The finer size allows better air-fuel mixing, which reduces pollutants like carbon monoxide and sulfur oxides. However, actual environmental impact depends on combustion technology and emission controls in place. Proper combustion management and emission reduction systems are essential regardless of coal size to meet environmental compliance standards.



